When you are choosing the right pet for your family, lifestyle, and purpose, you may be drawn to a particular breed of dog or cat, because their predictable traits make them a pet owner’s preferred choice. However, purebred pets can often come with the desired characteristics and a higher risk of certain breed-related health conditions. Understanding these potential health issues is crucial for responsible pet ownership, so you will know what to expect to ensure your furry friend receives the best possible care.
Common canine breed-related health conditions
Whether you choose a purebred pet for their fun-loving nature, strong work drive, or protective instincts, they will likely have many wonderful qualities, but also be prone to some breed-related health conditions, including:
Hip dysplasia in dogs
Hip dysplasia is a genetic condition where the hip joint does not form correctly, causing the ball-and-socket joint to rub and grind instead of moving smoothly, which can gradually lead to arthritis and pain.
While any breed can develop hip dysplasia, large- and giant-breed dogs are most commonly affected, including:
- German shepherds
- Labrador retrievers
- Golden retrievers
- Great Danes
- Newfoundlands
- Bernese mountain dogs
- Saint bernards
- Bulldogs
A dog who has hip dysplasia may have difficulty getting up, climbing or jumping into vehicles or on furniture, and may be reluctant to run and play, becoming irritable if their hips are touched.
Brachycephalic obstructive airway syndrome in dogs
Brachycephalic obstructive airway syndrome (BOAS) affects dogs with short noses and flat faces, who often have difficulty breathing because of their narrow nostrils, elongated soft palates, and small tracheas. Breeds most likely to suffer from BOAS include:
- French and English bulldogs
- Pugs
- Boston terriers
- Shih tzus
- Boxers
A dog with BOAS may snore, have labored breathing, exercise and heat intolerance, and difficulty eating. Some dogs may gag, retch, regurgitate, or vomit when trying to eat.
Dilated cardiomyopathy in dogs
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a heart muscle disease that leads to weakened heart contractions and poor blood circulation. Breeds most commonly affected by DCM include Doberman pinschers, boxers, Great Danes, and cocker spaniels.
If your dog develops DCM or other cardiac conditions, they may become lethargic, have difficulty breathing, cough, or faint.
Intervertebral disc disease in dogs
Intervertebral disc disease (IVDD) occurs when the cushioning discs between the vertebrae of the spinal column bulge or burst into the spinal cord space, causing pain, nerve damage, and possibly paralysis. Dogs with long backs and short legs are most commonly affected, including dachshunds, corgis, beagles, basset hounds, and shih tzus.
A dog who herniates a disc may display sudden back or neck pain, reluctance to move, and in severe cases, paralysis.
Common feline breed-related health conditions
Although purebred cats are less common than purebred dogs, many feline breeds make delightful family members. Consider the following breed-related health conditions if you are looking for a purebred cat to adopt or purchase:
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in cats
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a condition where the heart muscle thickens, making it difficult for the heart to pump blood efficiently. Breeds most commonly affected include Maine coons, ragdolls, and British shorthair cats.
A cat with HCM may suffer from lethargy, rapid breathing, open-mouth breathing, and sudden collapse.
Polycystic kidney disease in cats
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited disorder where cysts form in the kidneys, eventually leading to kidney failure. Breeds known to develop PKD include Persians, Himalayans, and British shorthairs.
A cat with PKD will show increased thirst and urination, weight loss, vomiting, and lethargy.
Progressive retinal atrophy in cats
Progressive retinal atrophy (PRA) is a group of genetic disorders that cause retinal degeneration, which leads to vision loss and blindness. Breeds affected include Abyssinians and Siamese cats.
A cat who suffers from retinal atrophy may display night blindness and dilated pupils.
Feline asthma
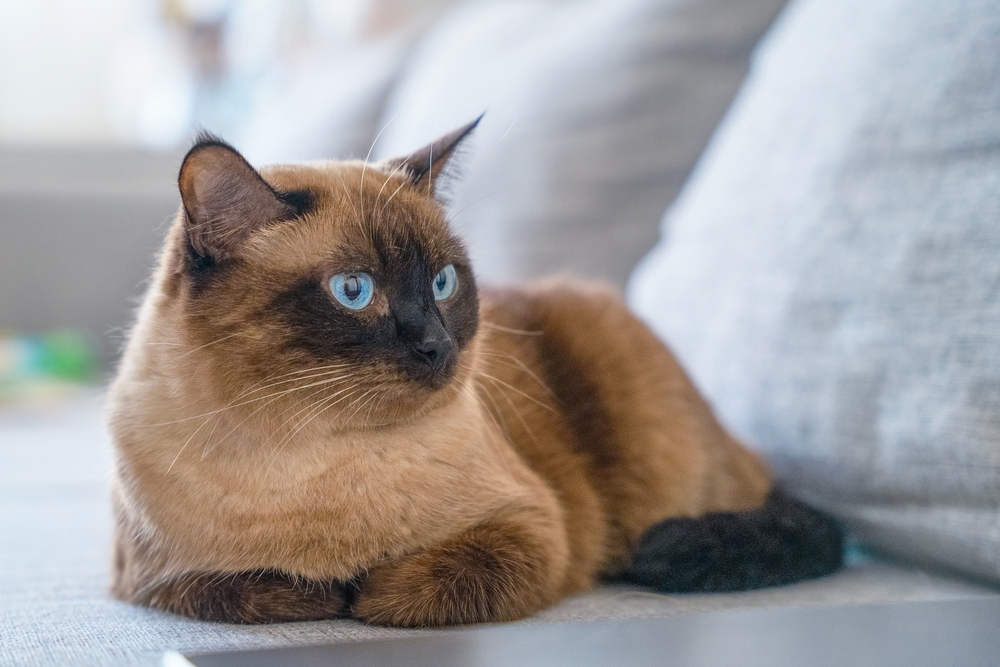

Feline asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the small airways in the lungs. Breeds most likely to develop asthma include Siamese cats and Oriental shorthairs.
A cat who develops feline asthma may cough, wheeze, have difficulty breathing, and breathe rapidly.
A purebred pet comes with the responsibility of understanding and managing breed-related health conditions, but you can support your dog or cat through regular preventive veterinary care. Schedule an appointment with our Chiefland Animal Hospital team to discuss the best way to keep your purebred pet healthy.






Leave A Comment